Page Contents:
Copyright - The exclusive and assignable legal right, given to the originator for a fixed number of years, to print, publish, perform, film or record material.
- Copyright of a musical work begins automatically once a piece of music is created and documented or recorded.
- Copyright is a matter of law - In the UK, this is detailed in the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.
- UK/EU copyright lasts for 70 years (starting from the end of the calendar year in which the creator dies).
- If the work originates from outside of the European Economic Area [EEA], it is protected by the copyright law of its own country and lasts for as long as specified in its country of origin, (if this does not exceed 70 years).
A Brief Timeline of Copyright

Who does Copyright Apply to & How can I tell if a work is in copyright?
There are 3 different types of copyrights to be aware of for a piece of music. Musical, Literary & Typographical. So:
- Musical: copyright of the actual music (notes in a certain order).
- Literary: copyright of the lyrics or libretto.
- Typographical: copyright of the published edition.
Copyright can include a number of different contributors:
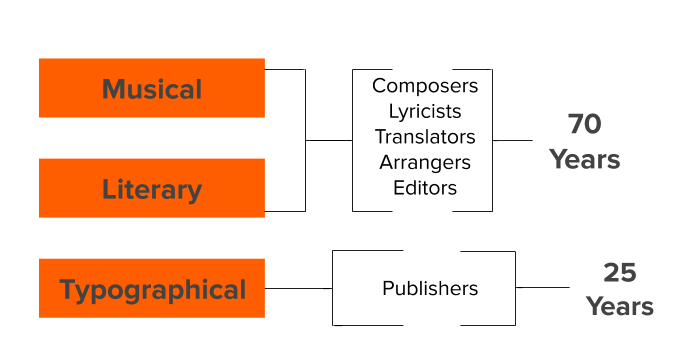
Example:
If a publisher decided to publish a new edition of William Rimmer’s Slaidburn, which is out of copyright, then their edition would then enter a 25-year long period of Copyright.
What is the difference between a music publisher and a printed music publisher?
A music publisher invests in intellectual property – in other words, it is only exploited when it is played, performed, copied or heard. One way of exploitation is by sheet music. The companies that make sheet music and songbooks are known as printed music publishers or print publishers.
Simply put: Music publishers invest in the intellectual property and printed music publishers make the sheet music and/or songbooks.
Sound Recordings
Sound Recordings also have a 70-year period in the EU. Copyright for sound recordings in the UK originally stood at 50 years from the end of the year the Sound Recording was made BUT some recording artists were finding that they were outliving their own copyright such as, Cliff Richard.
Example:
Darrol Barry died on 3 June 2018. The clock started ticking on the copyright status of his musical output after 11:59pm on 31st December 2018. Any music composed, edited or arranged by him is therefore still in copyright until 31 December 2088.